What is Basel III
Post on: 16 Март, 2015 No Comment
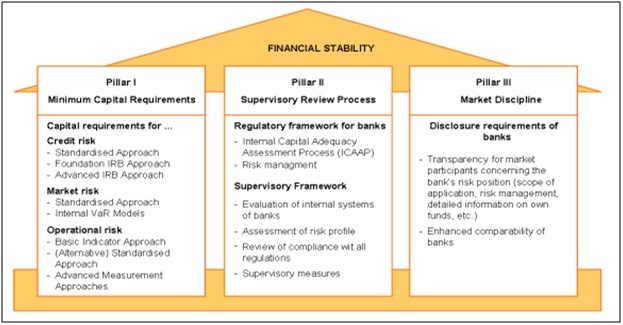
Hello, readers. Recently, I came across an article about ‘Basel III.’ Have you heard of this name, Basel? It is the third most populous city in Switzerland, located near the borders of France and Germany. The location, however, is not much of an importance this time. In fact, Basel III is a financial accord agreed upon by the Basel Committee on Banking Supervision (BCBS) in 2010. Also known as ‘The Third Basel Accord,’ it is an international regulatory framework for banks to strengthen the regulation, supervision and risk management of the banking sector.
The building of the Bank for International Settlements (BIS) in Basel
Well, apparently how I defined Basel III above is quite vague. It is indeed too technical to explain the whole sets of rules and regulations included in this accord. Thus, I would like to introduce this to you guys in more concrete and simple summary. Among many other things, the key word of this accord is the capital adequacy ratio recommended by the Bank for International Settlements (BIS). The higher the ratio is, the more stable the banks are. Banks with high ‘net worth’ rate are able to absorb shocks arising from financial and economic stress. So basically, the BCBS introduced the First Basel Accord in 1988, and amended its details in 2010 after several worldwide financial crises that originated from the United States.
The BIS capital adequacy ratio (in short, BIS ratio) is calculated as the above. Tier 1 and Tier 2 are the capital owned by the bank. Risk Weighted Assets are the bank’s assets weighed according to risk since different types of assets have different risk profiles. A class of asset such as debenture is considered to be a higher risk than cash or government bonds, for example.
So, back to the original topic, the Basel accords have set a guideline that banks need to meet at least 8 % of BIS ratio to ensure their financial soundness. Currently, most major international banks have met this guideline, and so do the major banks in Korea. In June 2011, the average of 17 domestic banks’ BIS ratios was 14.09%, [1] so they are generally in a sound state.
Still, there are two aspects of Basel III that are different from the former installments(Basel I and II).
① It framed new schemes called Liguidity Coverage Ratio(LCR) and Net Stable Funding Ratio(NSFR). These, put simply, are plans for banks to strengthen their liquidity so as to sustain in economic crisis.
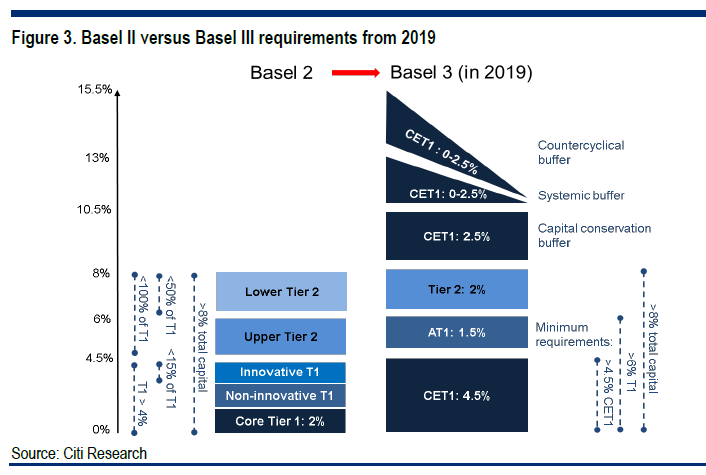
② While maintaining BIS ratio as 8 percent, it increased the risk-weight on the assets such as derivative transactions.
It was expected to be enforced from January 2013, but recently, it has been delayed by the financial authorities as other 16 member nations of the BCBS have not confirmed the framework to be carried out. Still, financial institutions in Korea have been getting ready for Basel 3 by increasing their net worth and reducing the amount of risk weighted assets. Besides, Financial Services Commission has put a lot of effort into making Basel 3 as effective as possible, segmenting the regulations on banks’ equity.
It is considered that it may slow down the banks’ growth due to the regulations. However, the Basel framework’s aim is to reduce the risk posed by unstable banks and promote banks’ transparency and disclosures, and by achieving so, we will have healthy bank sectors in Korea.
By Heeju Seo (shjundine@gmail.com)














