FAFSA Has a Different Idea About Your Assets
Post on: 9 Июль, 2015 No Comment
The federal methodology for determining a household’s total assets and net worth can be very complex for the family to figure out and plan for. There are certain investments and obligations which are not considered as assets to the government where college funds are concerned, and there are places that you can have extra money that are considered as fair game to the financial aid administrator. Below, you will find a generalized explanation of the basic guidelines that you should try to follow in order to keep your assets FAFSA friendly upon application for need-based aid through from government.
It may be easier to begin by listing the assets and savings that the FAFSA board will not consider as assessable income for the family or the student. These include annuities, cash value life insurance policies, equity value in the primary home residence, the family farm, personal assets and items such as household furniture, collections, clothing and the like, and retirement accounts. Your 401K, IRA, SEP, Keogh, or any other type of retirement savings are safe from being counted as assets.
The savings and assets which are considered as income of both the family and the student are as follows: trusts, limited partnerships, stocks, bonds, tax-exempt bonds, money market accounts, mutual funds, US savings bonds, custodial accounts, certificates of deposit, checking and savings accounts, investment properties, vacation homes, farm equipment and assets, and business assets and equipment. There are ways that you can offset the assessed value of real property assets, such as owing mortgage amounts on vacation homes or having a margin account loan through your broker.
Where trust funds and custodial accounts are concerned, the government will not assess the entire amount as income unless the account is the sole possession of either the student or parent. In cases where a trust or custodial account is in place for multiple people, a financial consultant may need to be involved in order to balance the amount of moneys belonging to the student and/or the parents. Once all disposable assets have been calculated by the FAFSA administrator, the next set of rules governing financial aid assessment will come into play. The federal law allows for an asset protection allowance to help ensure the future stability of the family’s income.
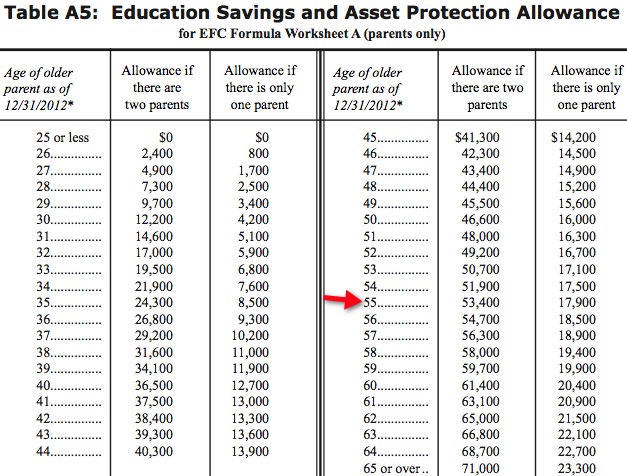
This is determined by not only the total assessed income of the family, but by the age of the parent(s) both at the time of application, and at the time of projected graduation. The older the parents are, the more asset protection allowance is calculated toward the end result. Whatever way you choose to position your assets in order to achieve the best financial aid results for your situation, be sure that all changes and arrangements are fully in effect for t least 12 months before filling out the FAFSA application. This is especially true for separated or divorced parents, where the income of the parent with whom the dependent has lived for the past year will be the determining factor.
Posted by bj on at
Filed under Additional Articles Tagged with














