Bonds Duration Bond Duration Duration Bond
Post on: 16 Март, 2015 No Comment
Bonds Duration
What is Duration , how is it used,and whats its significance in finance ?
We Answered:
In any analysis of fixed income (or liabilities), it is important to measure the “duration” of the income (or liability) stream. Duration is the cash-flow adjusted effective term to maturity for a series of given cash flows. Thus, duration is also sometimes referred to as “effective maturity.” It is also important to know that the duration of a portfolio of assets (or liabilities) is equal to the weighted average duration of the underlying assets (or liabilities). In addition, the higher the duration of a series of cash flows, the greater its sensitivity to a change in interest rates.
There are a variety of ways to calculate duration that are beyond the scope of this brief; however, most involve either a simple calculation heuristic or an automated spreadsheet. Either way, there is a very important benefit of knowing the duration of a series of cash flows. A bondholder that holds (and reinvests the coupons of) a bond to its duration is effectively “immunized” from interest rate changes and should experience a holding period yield (HPY) that is approximately equivalent to the original yield to maturity on the bond.
Of course, there are several assumptions (e.g. the bond issuer does not default, etc). However, in the base case, this notion can be very valuable to an investment manager that needs a certain cash flow at a certain date and time. This is often the case for endowments that have payout requirements or pensions that have retirement obligations.
If an investment manager can calculate the duration of its assets and the duration of its liabilities, it can make a determination as to the interest rate sensitivity of the portfolio; and thus estimate its ability to meet its future obligations. For example, if the duration of the portfolio assets is greater than the duration of the portfolio liabilities, then the portfolio structure is susceptible to rising interest rates.
This is because the higher duration assets are more sensitive to interest rates than the lower duration liabilities. Should interest rates rise, the assets will decline in value more quickly than the liabilities will. If interest rates remain at that level, there may be a shortfall in funding the liabilities.
One way to mitigate this problem is to rebalance the asset portfolio such that the duration of the assets is equal to the duration of the liabilities, such that any interest rate change has a negligible effect. If, in the case above, the asset portfolio duration is too high, the duration must be reduced.
This reduction may be accomplished by either rebalancing the portfolio with shorter duration assets (e.g. shorter term Treasuries or even cash) or by shorting longer duration assets. The zero coupon market in Treasuries (STRIPS) is often used due to the unique result that zero coupon bonds have durations that are exactly equivalent to their maturities.
When the duration of the portfolio of assets and the portfolio of liabilities is equivalent, changes in interest rates should have a negligible effect on the structure: the portfolio is said to be duration matched.
Mattie Said:
what is a yield to maturity. When is it used to value bonds ?What is bond duration ?Explain in terms of layman?
We Answered:
The yield to maturity is an interest rate. It is an IRR (Internal Rate of Return). If you find the present value of each cash flow, discounted at the yield — then the sum of those values is equal to the price of the bond.
To find the Present Value of a single cash flow, use this formula:
PV = C/(1+r)^N
Here C is the payment you receive
r is the one period discount rate (for US bonds, r = y/2 — we divide by two because there are two compounding periods per year.
N is the number of periods until you get the cash flow.
Bond Duration is a measure of price sensitivity. If yields go up,then bond prices go down (and if yield goes down then prices go up). The duration tells you how much it should go up or down. From a mathematical point of view, the modified duration is:
Mod Dur = -(dP/dy)/P — where P is Price as a function of yield — if you don't know any Calculus, ignore this comment)
That is, the duration is the percent change in price for a small change in yield.
Jeff410's definition of duration is incorrect. He may be confusing Duration with time to Maturity.
Charles Said:
why does a bonds convexity and duration increase with lower coupons and lower yields?
We Answered:
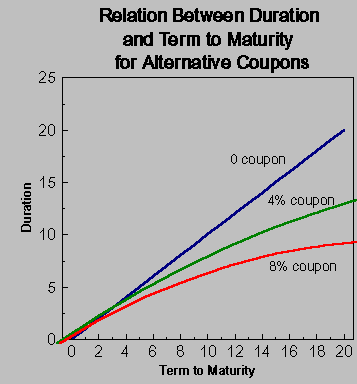
Duration is the weighted average term to maturity of a bonds cash flows. In other words, the higher the coupon the lower the duration, all other things being equal. A 10 yr. junk bond will have a lower duration than a 10 yr. government because of the higher coupon. Zero coupon bonds have the highest duration, all things being equal. Also, duration is affected by time to maturity. So 10 yr bond will have a higher duration than a 5 year bond, all other things equal.
Convexity is measuring the rate of change in duration as yields change. Most bonds have a positive convexity meaning its moves in tandem with duratiion.
Mae Said:
Duration is commonly used as a measure of interest rate risk for individual bonds as well as for portfolios of?














