Asset and liability management
Post on: 7 Май, 2015 No Comment
ASSET AND LIABILITY MANAGEMENT
In banking, asset and liability management (ALM) is used to manage the risks that arise due to mismatches between the assets and liabilities (debts and assets) of the bank.
Banks face several risks like the liquidity risk, market risk, interest rate risk, credit risk and operational risk. Asset Liability management (ALM) is a strategic management tool to manage interest rate risk and liquidity risk faced by banks, other financial services companies and corporations.
Banks manage the risks of Asset liability mismatch by matching the assets and liabilities according to the maturity pattern or the matching the duration, by hedging and by securitization.
Asset and liability management remain high-priority areas for bank regulators, with an emphasis on management of market risk, liquidity risk, and credit risk. Asset/liability managers face the challenge of keeping pace with industry changes as new areas of risk are identified and new tools and models are developed to help measure and manage risk.
In other words Asset-Liability Management (ALM) can be known as a risk management technique designed to earn an adequate return while maintaining a comfortable surplus of assets beyond liabilities. It takes into consideration interest rates, earning power, and degree of willingness to take on debt and hence is also known as Surplus Management.
But in the last decade the meaning of asset liability management has evolved. It is now used in many different ways under different contexts. ALM, which was actually pioneered by financial institutions and banks, are now widely being used in industries too. The Society of Actuaries Task Force on ALM Principles, Canada, offers the following definition for ALM: Asset Liability Management is the on-going process of formulating, implementing, monitoring, and revising strategies related to assets and liabilities in an attempt to achieve financial objectives for a given set of risk tolerances and constraints.
Basis of Asset-Liability Management
Traditionally, banks and insurance companies used accrual system of accounting for all their assets and liabilities. They would take on liabilities — such as deposits, life insurance policies or annuities. They would then invest the proceeds from these liabilities in assets such as loans, bonds or real estate. All these assets and liabilities were held at book value. Doing so disguised possible risks arising from how the assets and liabilities were structured.
Consider a bank that borrows 1 Crore (100 Lakhs) at 6 % for a year and lends the same money at 7 % to a highly rated borrower for 5 years. The net transaction appears profitable the bank is earning a 100 basis point spread but it entails considerable risk. At the end of a year, the bank will have to find new financing for the loan, which will have 4 more years before it matures. If interest rates have risen, the bank may have to pay a higher rate of interest on the new financing than the fixed 7 % it is earning on its loan.
Suppose, at the end of a year, an applicable 4-year interest rate is 8 %. The bank is in serious trouble. It is going to earn 7 % on its loan but would have to pay 8 % on its financing. Accrual accounting does not recognize this problem. Based upon accrual accounting, the bank would earn Rs 100,000 in the first year although in the preceding years it is going to incur a loss.
The problem in this example was caused by a mismatch between assets and liabilities. Prior to the 1970’s, such mismatches tended not to be a significant problem. Interest rates in developed countries experienced only modest fluctuations, so losses due to asset-liability mismatches were small or trivial. Many firms intentionally mismatched their balance sheets and as yield curves were generally upward sloping, banks could earn a spread by borrowing short and lending long.
Things started to change in the 1970s, which ushered in a period of volatile interest rates that continued till the early 1980s. US regulations which had capped the interest rates so that banks could pay depositors, was abandoned which led to a migration of dollar deposit overseas. Managers of many firms, who were accustomed to thinking in terms of accrual accounting, were slow to recognize this emerging risk. Some firms suffered staggering losses. Because the firms used accrual accounting, it resulted in more of crippled balance sheets than bankruptcies. Firms had no options but to accrue the losses over a subsequent period of 5 to 10 years.
One example, which drew attention, was that of US mutual life insurance company The Equitable. During the early 1980s, as the USD yield curve was inverted with short-term interest rates sky rocketing, the company sold a number of long-term Guaranteed Interest Contracts (GICs) guaranteeing rates of around 16% for periods up to 10 years.Equitable then invested the assets short-term to earn the high interest rates guaranteed on the contracts. But short-term interest rates soon came down. When the Equitable had to reinvest, it couldn’t get even close to the interest rates it was paying on the GICs. The firm was crippled. Eventually, it had to demutualize and was acquired by the Axa Group.
Increasingly banks and asset management companies started to focus on Asset-Liability Risk.The problem was not that the value of assets might fall or that the value of liabilities might rise. It was that capital might be depleted by narrowing of the difference between assets and liabilities and that the values of assets and liabilities might fail to move in tandem. Asset-liability risk is predominantly a leveraged form of risk.
The capital of most financial institutions is small relative to the firm’s assets or liabilities, and so small percentage changes in assets or liabilities can translate into large percentage changes in capital. Accrual accounting could disguise the problem by deferring losses into the future, but it could not solve the problem.Firms responded by forming asset-liability management (ALM) departments to assess these asset-liability risk.
Techniques for assessing Asset-Liability Risk
Techniques for assessing asset-liability risk came to include Gap Analysis and Duration Analysis. These facilitated techniques of managing gaps and matching duration of assets and liabilities. Both approaches worked well if assets and liabilities comprised fixed cash flows. But cases of callable debts, home loans and mortgages which included optio.ns of prepayment and floating rates, posed problems that gap analysis could not address. Duration analysis could address these in theory, but implementing sufficiently sophisticated duration measures was problematic Accordingly, banks and insurance companies started using Scenario Analysis.
Under this technique assumptions were made on various conditions, for example: -
* Several interest rate scenarios were specified for the next 5 or 10 years. These specified conditions like declining rates, rising rates, a gradual decrease in rates followed by a sudden rise, etc. Ten or twenty scenarios could be specified in all.
* Assumptions were made about the performance of assets and liabilities under each scenario. They included prepayment rates on mortgages or surrender rates on insurance products.
* Assumptions were also made about the firm’s performance-the rates at which new business would be acquired for various products, demand for the product.
* Market conditions and economic factors like inflation rates and industrial cycles were also included.
* Based upon these assumptions, the performance of the firm’s balance sheet could be projected under each scenario. If projected performance was poor under specific scenarios, the ALM committee would adjust assets or liabilities to address the indicated exposure. Let us consider the procedure for sanctioning a commercial loan. The borrower, who approaches the bank, has to appraise the banks credit department on various parameters like industry prospects, operational efficiency, financial efficiency, management qualities and other things, which would influence the working of the company. On the basis of this appraisal, the banks would then prepare a credit-grading sheet after covering all the aspects of the company and the business in which the company is in. Then the borrower would then be charged a certain rate of interest, which would cover the risk of lending.
* But the main shortcoming of scenario analysis was that, it was highly dependent on the choice of scenarios. It also required that many assumptions were to be made about how specific assets or liabilities will perform under specific scenario. Gradually the firms recognized a potential for different type of risks, which was overlooked in ALM analyses. Also the deregulation of the interest rates in US in mid 70 s compelled the banks to undertake active planning for the structure of the balance sheet. The uncertainty of interest rate movements gave rise to Interest Rate Risk thereby causing banks to look for processes to manage this risk. In the wake of interest rate risk came Liquidity Risk and Credit Risk, which became inherent components of risk for banks. The recognition of these risks brought Asset Liability Management to the centre-stage of financial intermediation. Today even Equity Risk, which until a few years ago was given only honorary mention in all but a few company ALM reports, is now an indispensable part of ALM for most companies. Some companies have gone even further to include Counterparty Credit Risk, Sovereign Risk, as well as Product Design and Pricing Risk as part of their overall ALM.
* Now a day’s a company has different reasons for doing ALM. While some companies view ALM as a compliance and risk mitigation exercise, others have started using ALM as strategic framework to achieve the company’s financial objectives. Some of the business reasons companies now state for implementing an effective ALM framework include gaining competitive advantage and increasing the value of the organization.
Asset-Liability Management Approach
ALM in its most apparent sense is based on funds management. Funds management represents the core of sound bank planning and financial management. Although funding practices, techniques, and norms have been revised substantially in recent years, it is not a new concept. Funds management is the process of managing the spread between interest earned and interest paid while ensuring adequate liquidity. Therefore, funds management has following three components, which have been discussed briefly.
A. Liquidity Management
Liquidity represents the ability to accommodate decreases in liabilities and to fund increases in assets. An organization has adequate liquidity when it can obtain sufficient funds, either by increasing liabilities or by converting assets, promptly and at a reasonable cost. Liquidity is essential in all organizations to compensate for expected and unexpected balance sheet fluctuations and to provide funds for growth. The price of liquidity is a function of market conditions and market perception of the risks, both interest rate and credit risks, reflected in the balance sheet and off-balance sheet activities in the case of a bank. If liquidity needs are not met through liquid asset holdings, a bank may be forced to restructure or acquire additional liabilities under adverse market conditions. Liquidity exposure can stem from both internally (institution-specific) and externally generated factors. Sound liquidity risk management should address both types of exposure. External liquidity risks can be geographic, systemic or instrument-specific. Internal liquidity risk relates largely to the perception of an institution in its various markets: local, regional, national or international. Determination of the adequacy of a bank’s liquidity position depends upon an analysis of its: -
* Historical funding requirements
* Current liquidity position
* Anticipated future funding needs
* Sources of funds
* Present and anticipated asset quality
* Present and future earnings capacity
* Present and planned capital position
As all banks are affected by changes in the economic climate, the monitoring of economic and money market trends is key to liquidity planning. Sound financial management can minimize the negative effects of these trends while accentuating the positive ones. Management must also have an effective contingency plan that identifies minimum and maximum liquidity needs and weighs alternative courses of action designed to meet those needs. The cost of maintaining liquidity is another important prerogative. An institution that maintains a strong liquidity position may do so at the opportunity cost of generating higher earnings. The amount of liquid assets a bank should hold depends on the stability of its deposit structure and the potential for rapid expansion of its loan portfolio. If deposit accounts are composed primarily of small stable accounts, a relatively low allowance for liquidity is necessary.
Additionally, management must consider the current ratings by regulatory and rating agencies when planning liquidity needs. Once liquidity needs have been determined, management must decide how to meet them through asset management, liability management, or a combination of both.
B. Asset Management
Many banks (primarily the smaller ones) tend to have little influence over the size of their total assets. Liquid assets enable a bank to provide funds to satisfy increased demand for loans. But banks, which rely solely on asset management, concentrate on adjusting the price and availability of credit and the level of liquid assets. However, assets that are often assumed to be liquid are sometimes difficult to liquidate. For example, investment securities may be pledged against public deposits or repurchase agreements, or may be heavily depreciated because of interest rate changes. Furthermore, the holding of liquid assets for liquidity purposes is less attractive because of thin profit spreads.
Asset liquidity, or how salable the bank’s assets are in terms of both time and cost, is of primary importance in asset management. To maximize profitability, management must carefully weigh the full return on liquid assets (yield plus liquidity value) against the higher return associated with less liquid assets. Income derived from higher yielding assets may be offset if a forced sale, at less than book value, is necessary because of adverse balance sheet fluctuations.
Seasonal, cyclical, or other factors may cause aggregate outstanding loans and deposits to move in opposite directions and result in loan demand, which exceeds available deposit funds. A bank relying strictly on asset management would restrict loan growth to that which could be supported by available deposits. The decision whether or not to use liability sources should be based on a complete analysis of seasonal, cyclical, and other factors, and the costs involved. In addition to supplementing asset liquidity, liability sources of liquidity may serve as an alternative even when asset sources are available.
C. Liability Management
Liquidity needs can be met through the discretionary acquisition of funds on the basis of interest rate competition. This does not preclude the option of selling assets to meet funding needs, and conceptually, the availability of asset and liability options should result in a lower liquidity maintenance cost. The alternative costs of available discretionary liabilities can be compared to the opportunity cost of selling various assets. The major difference between liquidity in larger banks and in smaller banks is that larger banks are better able to control the level and composition of their liabilities and assets. When funds are required, larger banks have a wider variety of options from which to select the least costly method of generating funds. The ability to obtain additional liabilities represents liquidity potential. The marginal cost of liquidity and the cost of incremental funds acquired are of paramount importance in evaluating liability sources of liquidity. Consideration must be given to such factors as the frequency with which the banks must regularly refinance maturing purchased liabilities, as well as an evaluation of the bank’s ongoing ability to obtain funds under normal market conditions.
The obvious difficulty in estimating the latter is that, until the bank goes to the market to borrow, it cannot determine with complete certainty that funds will be available and/or at a price, which will maintain a positive yield spread. Changes in money market conditions may cause a rapid deterioration in a bank’s capacity to borrow at a favorable rate. In this context, liquidity represents the ability to attract funds in the market when needed, at a reasonable cost vis—vis asset yield. The access to discretionary funding sources for a bank is always a function of its position and reputation in the money markets.
Although the acquisition of funds at a competitive cost has enabled many banks to meet expanding customer loan demand, misuse or improper implementation of liability management can have severe consequences. Further, liability management is not riskless. This is because concentrations in funding sources increase liquidity risk. For example, a bank relying heavily on foreign interbank deposits will experience funding problems if overseas markets perceive instability in U.S. banks or the economy. Replacing foreign source funds might be difficult and costly because the domestic market may view the bank’s sudden need for funds negatively. Again over-reliance on liability management may cause a tendency to minimize holdings of short-term securities, relax asset liquidity standards, and result in a large concentration of short-term liabilities supporting assets of longer maturity. During times of tight money, this could cause an earnings squeeze and an illiquid condition.
Also if rate competition develops in the money market, a bank may incur a high cost of funds and may elect to lower credit standards to book higher yielding loans and securities. If a bank is purchasing liabilities to support assets, which are already on its books, the higher cost of purchased funds may result in a negative yield spread.
Preoccupation with obtaining funds at the lowest possible cost, without considering maturity distribution, greatly intensifies a bank’s exposure to the risk of interest rate fluctuations. That is why banks who particularly rely on wholesale funding sources, management must constantly be aware of the composition, characteristics, and diversification of its funding sources.
Procedure for Examination of Asset Liability Management
In order to determine the efficacy of Asset Liability Management one has to follow a comprehensive procedure of reviewing different aspects of internal control, funds management and financial ratio analysis. Below a step-by-step approach of ALM examination in case of a bank has been outlined.
Step 1
The bank/ financial statements and internal management reports should be reviewed to assess the asset/liability mix with particular emphasis on.
* Total liquidity position (Ratio of highly liquid assets to total assets)
* Current liquidity position (Minimum ratio of highly liquid assets to demand liabilities/deposits)
* Ratio of Non Performing Assets to Total Assets
* Ratio of loans to deposits
* Ratio of short-term demand deposits to total deposits
* Ratio of long-term loans to short term demand deposits
* Ratio of contingent liabilities for loans to total loans
* Ratio of pledged securities to total securities
Step 2
It is to be determined that whether bank management adequately assesses and plans its liquidity needs and whether the bank has short-term sources of funds. This should include
* Review of internal management reports on liquidity needs and sources of satisfying these need..
* Assessing the bank’s ability to meet liquidity needs
Step 3
The banks future development and expansion plans, with focus on funding and liquidity management aspects has to be looked into. This entails.
* Determining whether bank management has effectively addressed the issue of need for liquid assets to funding sources on a long-term basis.
* Reviewing the bank’s budget projections for a certain period of time in the future.
* Determining whether the bank really needs to expand its activities. What are the sources of funding for such expansion and whether there are projections of changes in the bank’s asset and liability structure.
* Assessing the bank’s development plans and determining whether the bank will be able to attract planned funds and achieve the projected asset growth.
* Determining whether the bank has included sensitivity to interest rate risk in the development of its long term funding strategy.
Step 4
Examining the bank’s internal audit report in regards to quality and effectiveness in terms of liquidity management.
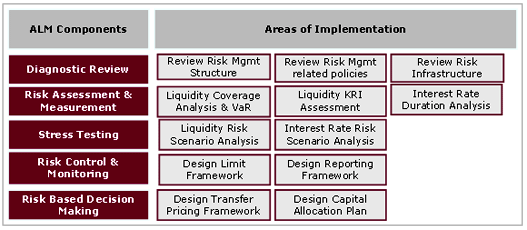
Step 5
Reviewing the bank’s plan of satisfying unanticipated liquidity needs by.
* Determining whether the bank’s management assessed the potential expenses that the bank will have as a result of unanticipated financial or operational problems.
* Determining the alternative sources of funding liquidity and/or assets subject to necessity.
* Determining the impact of the bank’s liquidity management on net earnings position.
Step 6
Preparing an Asset/Liability Management Internal Control Questionnaire which should include the following
Whether the board of directors has been consistent with its duties and responsibilities and included
o A line of authority for liquidity management decisions.
o A mechanism to coordinate asset and liability management decisions.
o A method to identify liquidity needs and the means to meet those needs.
o Guidelines for the level of liquid assets and other sources of funds in relationship to needs.
Does the planning and budgeting function consider liquidity requirements.
Are the internal management reports for liquidity management adequate in terms of effective decision making and monitoring of decisions.
Are internal management reports concerning liquidity needs prepared regularly and reviewed as appropriate by senior management and the board of directors.
Whether the bank’s policy of asset and liability management prohibits or defines certain restrictions for attracting borrowed means from bank related persons (organizations) in order to satisfy liquidity needs.
Does the bank’s policy of asset and liability management provide for an adequate control over the position of contingent liabilities of the bank.
Is the foregoing information considered an adequate basis for evaluating internal control in that there are no significant deficiencies in areas not covered in this questionnaire that impair any controls.
Guidelines on Asset-Liability Management (ALM) System -Amendments
Reserve Bank had issued guidelines on ALM system vide Circular dated February 10, 1999, which covered, among others, interest rate risk and liquidity risk measurement / reporting framework and prudential limits. As a measure of liquidity management, banks are required to monitor their cumulative mismatches across all time buckets in their Statement of Structural Liquidity by establishing internal prudential limits with the approval of the Board / Management Committee. As per the guidelines, the mismatches (negative gap) during the time buckets of 1-14 days and 15-28 days in the normal course, are not to exceed 20 per cent of the cash outflows in the respective time buckets.
2. Having regard to the international practices, the level of sophistication of banks in India and the need for a sharper assessment of the efficacy of liquidity management, Reserve Bank of India has reviewed guidelines on 24th October 2007 and decided that :
(a) the banks may adopt a more granular approach to measurement of liquidity risk by splitting the first time bucket (1-14 days at present) in the Statement of Structural Liquidity into three time buckets viz. Next day. 2-7 days and 8-14 days.
(b) the Statement of Structural Liquidity may be compiled on best available data coverage, in due consideration of non-availability of a fully networked environment.Banks may, however, make concerted and requisite efforts to ensure coverage of 100 per cent data in a timely manner.
(c) the net cumulative negative mismatches during the Next day, 2-7 days, 8-14 days and 15-28 days buckets should not exceed 5 % ,10%, 15 % and 20 % of the cumulative cash outflows in the respective time buckets in order to recognise the cumulative impact on liquidity.
(d) banks may undertake dynamic liquidity management and should prepare the Statement of Structural Liquidity on daily basis. The Statement of Structural Liquidity, may, however, be reported to RBI, once a month, as on the third Wednesday of every month.
3. The format of Statement of Structural Liquidity has been revised suitably and is furnished. The guidance for slotting the future cash flows of banks in the revised time buckets has also been suitably modified and is furnished at Annex II.
4. To enable the banks to fine tune their existing MIS as per the modified guidelines, the revised norms as well as the supervisory reporting as per the revised format would commence with effect from the period beginning January 1, 2008 and the reporting frequency would continue to be monthly for the present. However, the frequency of supervisory reporting of the Structural Liquidity position shall be fortnightly, with effect from the fortnight beginning April 1, 2008.
Asset Liability Management in Indian Context
The post-reform banking scenario in India was marked by interest rate deregulation, entry of new private banks, and gamut of new products along with greater use of information technolog.To cope with these pressures banks were required to evolve strategies rather than ad hoc solutions. Recognising the need of Asset Liability management to develop a strong and sound banking.system, the RBI has come out with ALM guidelines for banks and FIs in April 1999.The Indian ALM framework rests on three pillars.
ALM Organisation (ALCO)
The ALCO or the Asset Liability Management Committee consisting of the banks senior management including the CEO should be responsible for adhering to the limits set by the board as well as for deciding the business strategy of the bank in line with the banks budget and decided risk management objectives. ALCO is a decision-making unit responsible for balance sheet planning from a risk return perspective including strategic management of interest and liquidity risk. The banks may also authorise their Asset-Liability Management Committee (ALCO) to fix interest rates on Deposits and Advances, subject to their reporting to the Board immediately thereafter. The banks should also fix maximum spread over the PLR with the approval of the ALCO/Board for all advances other than consumer credit.
ALM Information System
The ALM Information System is required for the collection of information accurately, adequately and expeditiously. Information is the key to the ALM process. A good information system gives the bank management a complete picture of the bank’s balance sheet.
ALM Process
The basic ALM processes involving identification, measurement and management of risk parameter.The RBI in its guidelines has asked Indian banks to use traditional techniques like Gap Analysis for monitoring interest rate and liquidity risk. However RBI is expecting Indian banks to move towards sophisticated techniques like Duration, Simulation, VaR in the future. For the accrued portfolio, most Indian Private Sector banks use Gap analysis, but are gradually moving towards duration analysis. Most of the foreign banks use duration analysis and are expected to move towards advanced methods like Value at Risk for the entire balance sheet.some foreign banks are already using VaR for the entire balance sheet.
Conclusion
ALM has evolved since the early 1980’s.Today, financial firms are increasingly using market value accounting for certain business lines. This is true of universal banks that have trading operations.Techniques of ALM have also evolved.The growth of OTC derivatives markets has facilitated a variety of hedging strategies. A significant development has been securitization, which allows firms to directly address asset-liability risk by removing assets or liabilities from their balance sheets. This not only eliminates asset-liability risk; it also frees up the balance sheet for new business.
Thus, the scope of ALM activities has widened. Today, ALM departments are addressing (non-trading) foreign exchange risks as well as other risks. Also, ALM has extended to non-financial firms. Corporations have adopted techniques of ALM to address interest-rate exposures, liquidity risk and foreign exchange risk. They are using related techniques to address commodities risks. For example, airlines’ hedging of fuel prices or manufacturers’ hedging of steel prices are often presented as ALM. Thus it can be safely said that Asset Liability Management will continue to grow in future and an efficient ALM technique will go a long way in managing volume, mix, maturity, rate sensitivity, quality and liquidity of the assets and liabilities so as to earn a sufficient and acceptable return on the portfolio.














